Which of the following statements is true of REM sleep? REM sleep, characterized by vivid dreams, rapid eye movements, and muscle paralysis, plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and creativity. This article delves into the unique characteristics, brain activity, disorders, and effects of sleep deprivation on REM sleep, providing a comprehensive understanding of this essential sleep stage.
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep: Characteristics and Role: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Rem Sleep
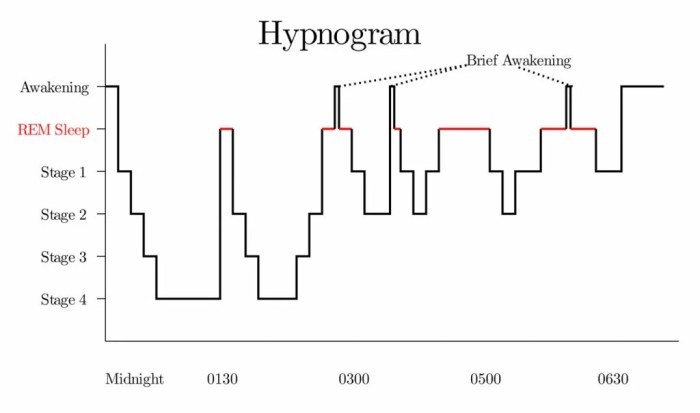
REM sleep is a distinct stage of sleep characterized by vivid dreams, rapid eye movements, and muscle paralysis. It plays a crucial role in memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and creativity.
Unique Characteristics of REM Sleep
Vivid dreams
REM sleep is associated with the most intense and memorable dreams.
Rapid eye movements
The eyes move rapidly under the eyelids during REM sleep.
Muscle paralysis
The muscles of the body, except for the diaphragm and extraocular muscles, are paralyzed during REM sleep, preventing dream-related movements.
Role of REM Sleep
Memory consolidation
REM sleep is essential for the consolidation of memories, particularly procedural and episodic memories.
Emotional regulation
REM sleep helps regulate emotions by processing and reducing the intensity of emotional experiences.
Creativity
REM sleep has been linked to enhanced creativity and problem-solving abilities.
REM Sleep and Brain Activity
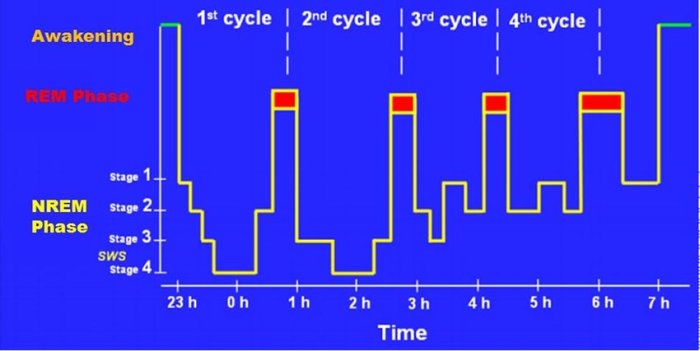
REM sleep involves specific brain regions and neural mechanisms:
Brain Regions Involved in REM Sleep, Which of the following statements is true of rem sleep
Pontine reticular formation
Responsible for generating the muscle paralysis associated with REM sleep.
Locus coeruleus
Regulates the rapid eye movements and arousal during REM sleep.
Raphe nuclei
Involved in the production of serotonin, which promotes REM sleep.
Neural Mechanisms
EEG patterns
REM sleep is characterized by low-amplitude, high-frequency EEG waves known as theta waves.
Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine and serotonin play significant roles in regulating REM sleep. Acetylcholine promotes REM sleep, while serotonin inhibits it.
REM Sleep Disorders
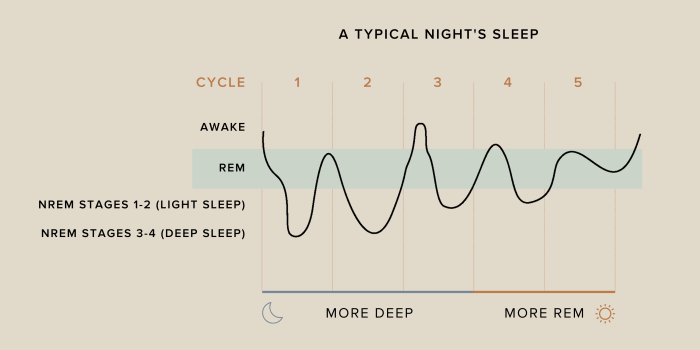
Common REM sleep disorders include:
Narcolepsy
- Characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden sleep attacks.
- REM sleep may occur at inappropriate times during the day.
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
Involves acting out dreams during REM sleep, which can lead to injuries or harm to others.
Sleep Apnea
Causes pauses in breathing during sleep, which can disrupt REM sleep.
REM Sleep and Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation can significantly affect REM sleep:
Effects on REM Sleep Patterns
- Reduced duration and frequency of REM sleep.
- Altered EEG patterns during REM sleep.
Consequences of REM Sleep Loss
- Cognitive impairment, including memory deficits and difficulty concentrating.
- Emotional instability and increased risk of mood disorders.
- Physiological problems, such as increased inflammation and weakened immune function.
Strategies for Improving REM Sleep
- Establish regular sleep-wake cycles.
- Create a conducive sleep environment.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bed.
- Engage in relaxing activities before sleep.
- Seek professional help if experiencing persistent REM sleep problems.
Popular Questions
What is the main function of REM sleep?
REM sleep is primarily involved in memory consolidation, emotional regulation, and creativity.
What are the characteristic features of REM sleep?
REM sleep is characterized by vivid dreams, rapid eye movements, and muscle paralysis.
What are some common REM sleep disorders?
Common REM sleep disorders include narcolepsy, REM sleep behavior disorder, and sleep apnea.