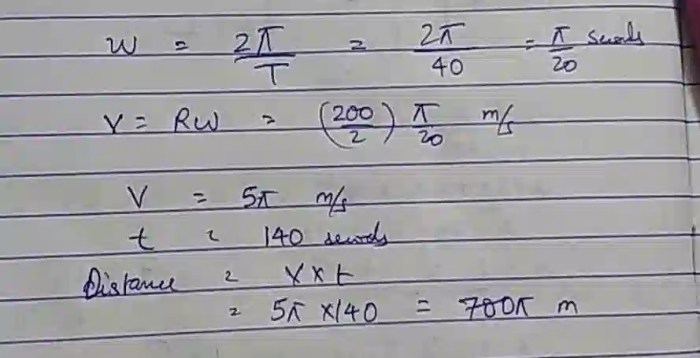An elevator accelerates upward at 1.2 m/s2 – In the realm of physics, acceleration takes center stage as an elevator embarks on an upward journey, accelerating at a steady rate of 1.2 m/s2. This motion sets the stage for a captivating exploration of kinematics, unraveling the intricate relationship between acceleration, velocity, and distance.
As the elevator ascends, its velocity undergoes a continuous transformation, increasing with each passing moment. The formula v = u + at, where u represents the initial velocity, a symbolizes acceleration, and t denotes time, governs this change. By employing this equation, we can precisely calculate the elevator’s velocity at any given time interval.
Elevator Acceleration
Acceleration is a measure of the rate at which an object’s velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of acceleration is expressed in meters per second squared (m/s 2), and the direction is indicated by a plus or minus sign.
A positive acceleration indicates that the object’s velocity is increasing, while a negative acceleration indicates that the object’s velocity is decreasing.
Elevator Velocity
Velocity is a measure of the rate at which an object moves. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction. The magnitude of velocity is expressed in meters per second (m/s), and the direction is indicated by a plus or minus sign.
A positive velocity indicates that the object is moving in the positive direction, while a negative velocity indicates that the object is moving in the negative direction.
The relationship between acceleration and velocity is given by the following equation:
v = u + at
where:
- v is the final velocity (m/s)
- u is the initial velocity (m/s)
- a is the acceleration (m/s 2)
- t is the time (s)
Distance Traveled
The distance traveled by an object is the total length of the path that the object has traveled. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude. The magnitude of distance is expressed in meters (m).
The relationship between acceleration, velocity, and distance is given by the following equation:
s = ut + 1/2 at2
where:
- s is the distance traveled (m)
- u is the initial velocity (m/s)
- a is the acceleration (m/s 2)
- t is the time (s)
Forces Acting on the Elevator: An Elevator Accelerates Upward At 1.2 M/s2
The forces acting on an elevator are:
- Gravity (mg)
- Tension in the cable (T)
- Normal force from the elevator floor (N)
The direction and magnitude of each force is as follows:
- Gravity is a downward force equal to the mass of the elevator times the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s 2).
- Tension in the cable is an upward force equal to the weight of the elevator.
- Normal force from the elevator floor is an upward force equal to the weight of the elevator.
Passenger Experience
The passengers in an elevator experience a variety of sensations as the elevator accelerates. These sensations include:
- A feeling of weightlessness as the elevator accelerates upward
- A feeling of increased pressure on the body as the elevator accelerates downward
- A feeling of nausea or dizziness if the acceleration is too great
These sensations are caused by the changes in the forces acting on the body as the elevator accelerates.
Elevator Design
The design of an elevator is a complex process that must take into account a variety of factors, including:
- The number of passengers the elevator will carry
- The speed of the elevator
- The height of the building
- The safety features that must be incorporated into the elevator
Elevators are typically designed with a variety of safety features, including:
- Emergency brakes
- Over-speed governors
- Door interlocks
FAQs
What is the significance of acceleration in elevator motion?
Acceleration is a crucial factor in elevator motion as it determines the rate at which the elevator’s velocity changes. A positive acceleration, as in the case of an upward-moving elevator, indicates an increase in velocity over time.
How does acceleration affect the passenger experience in an elevator?
Acceleration can induce sensations of weightlessness or increased pressure on the body, depending on the direction and magnitude of the acceleration. In an upward-accelerating elevator, passengers may experience a slight feeling of lightness.