The presence of many C-C and C-H bonds forms the backbone of organic chemistry, shaping the structure, properties, and reactivity of countless compounds. This article delves into the intricate world of these bonds, exploring their types, properties, importance, and applications.
C-C bonds, formed between two carbon atoms, and C-H bonds, formed between a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom, are the most abundant bonds in organic molecules. They determine the molecular architecture, influence physical and chemical properties, and dictate the reactivity of these compounds.
Types of C-C and C-H Bonds: The Presence Of Many C-c And C-h Bonds
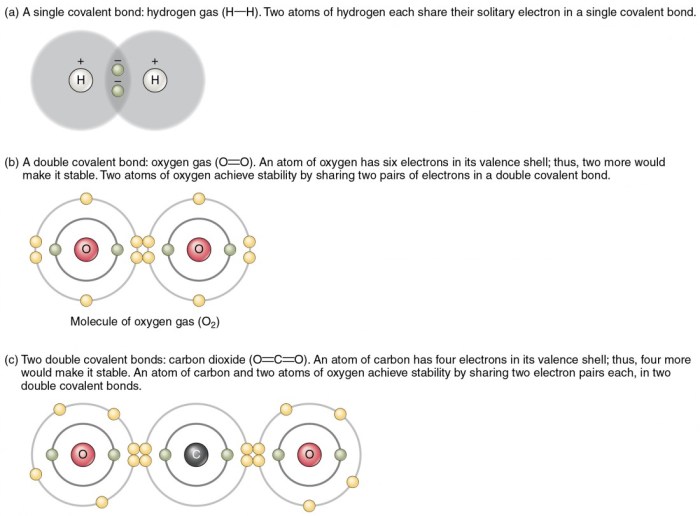
C-C bonds are formed between two carbon atoms, while C-H bonds are formed between a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom. There are different types of C-C and C-H bonds, depending on the hybridization of the carbon atom involved.
Types of C-C Bonds
- Single bond (C-C): Formed by the overlap of one sp 3orbital from each carbon atom.
- Double bond (C=C): Formed by the overlap of two sp 2orbitals from each carbon atom.
- Triple bond (C≡C): Formed by the overlap of three sp orbitals from each carbon atom.
Types of C-H Bonds
- C-H bond: Formed by the overlap of an sp 3orbital from the carbon atom and an s orbital from the hydrogen atom.
Properties of C-C and C-H Bonds
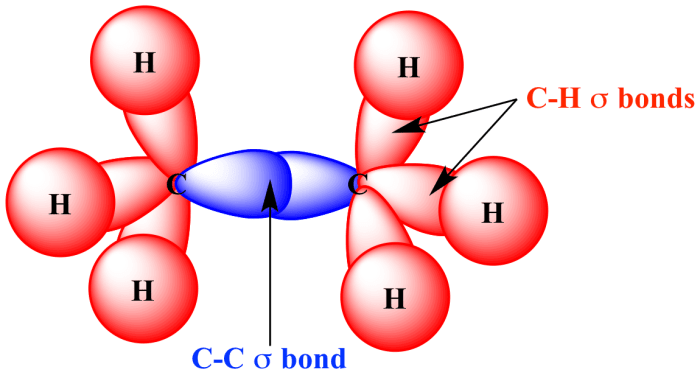
The properties of C-C and C-H bonds depend on the type of bond and the hybridization of the carbon atom involved.
Properties of C-C Bonds, The presence of many c-c and c-h bonds
- Bond length: Single bonds are the longest, followed by double bonds and then triple bonds.
- Bond strength: Triple bonds are the strongest, followed by double bonds and then single bonds.
- Bond polarity: Single bonds are nonpolar, while double and triple bonds are polar.
Properties of C-H Bonds
- Bond length: C-H bonds are typically shorter than C-C bonds.
- Bond strength: C-H bonds are weaker than C-C bonds.
- Bond polarity: C-H bonds are polar, with the hydrogen atom being slightly positive and the carbon atom being slightly negative.
Questions and Answers
What are the different types of C-C and C-H bonds?
C-C bonds can be single, double, or triple, while C-H bonds can be classified as primary, secondary, tertiary, or aromatic.
How do C-C and C-H bonds affect the properties of organic molecules?
C-C bonds contribute to the strength and rigidity of the molecular framework, while C-H bonds influence polarity, solubility, and reactivity.
What spectroscopic techniques can be used to identify C-C and C-H bonds?
Infrared (IR) spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and mass spectrometry are commonly used techniques for identifying and characterizing these bonds.